Air-Gapped Environments
Distr supports air-gapped environments where strict security requirements demand physical or logical isolation from public networks. This deployment model is ideal for organizations in regulated industries, such as defense, finance, and critical infrastructure, where external connectivity or the use of agents is not permitted.
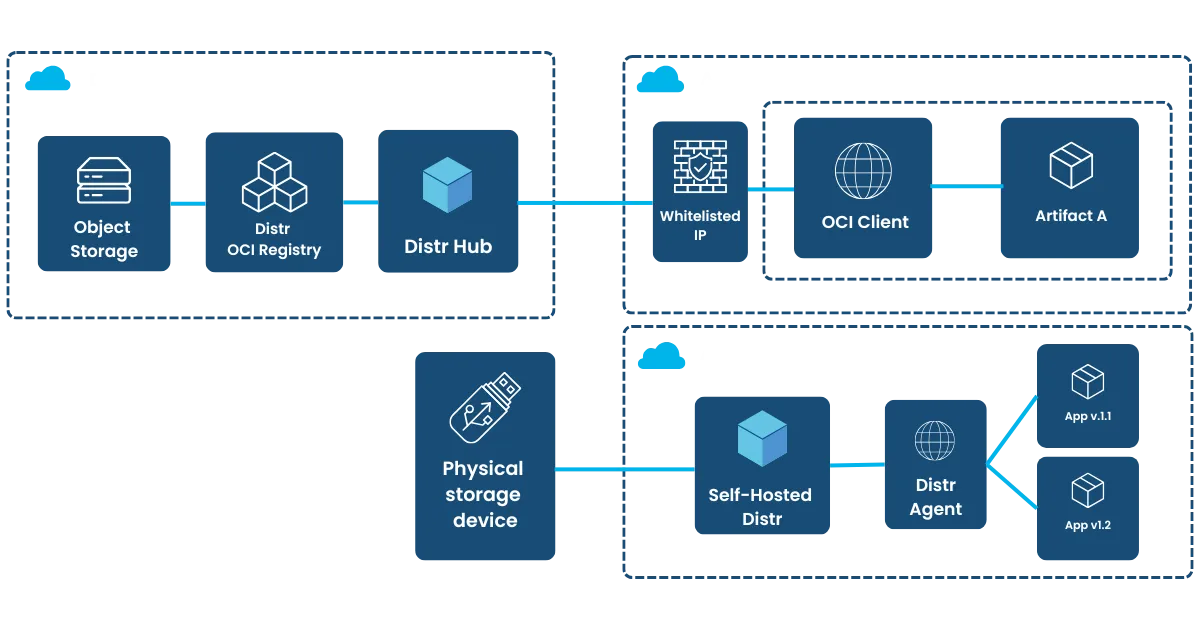
Distr offers two approaches to support these environments:
- IP Whitelisting: For environments that can allow limited outbound connections.
- Self-Managed Registry with Physical Transfers: For fully isolated environments, Distr supports a workflow where updates are packaged, encrypted, and physically transferred (e.g., via USB or secure media).
Solution Architecture
Section titled “Solution Architecture”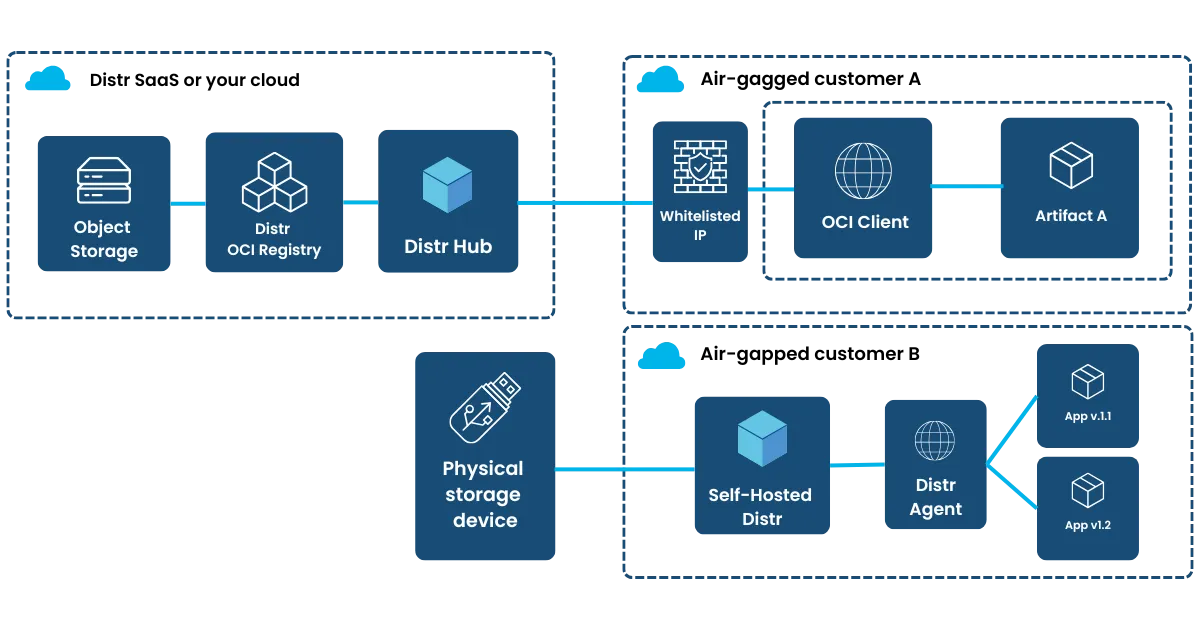
Implementation Steps
Section titled “Implementation Steps”- Set Up Your Registry
- Onboard Your Application
- White-label the Customer portal
- Onboard your first customer
- Request IP Allowlist for Customer Access
- Customer creates a Personal Access token
- Customer can access and pull your private artifacts
- End-customer self hosts Distr in their internal environment
- Vendors deliver media to customer environment to be deployed internally via Distr
- Reach out to support@glasskube.com for more detailed information of how Distr can enable this end-customer use case