Artifact Registry
The Distr Artifact Registry is a built-in, OCI-compliant registry designed for AI and software companies to distribute Docker images and Helm Charts, SBOMs and other OCI artifacts to self-managed and BYOC environments. It features advanced tag-based access and licensing controls. The registry also provides detailed download analytics that let you monitor which versions of your software are being used by each customer.
Use it to publish versioned artifacts, enforce licensing rules, and track consumption across your customer base.
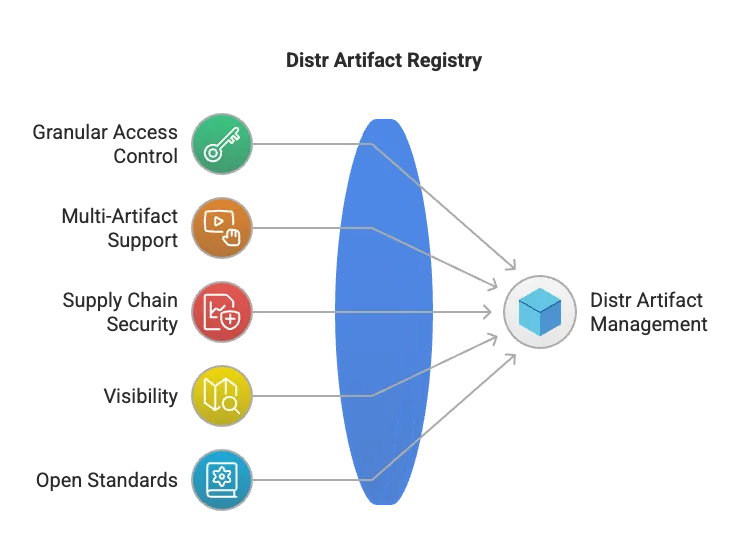
Core capabilities
Section titled “Core capabilities”- Multi-artifact support: Distribute Docker Images, Helm Charts, Terraform Modules, and any OCI-compliant artifact
- Software supply chain security: Store SBOMs and signatures for image verification
- Visibility: Get insights into which customers are using which artifacts and versions
- Open standards: Built on the OCI specification and compatible with existing tooling (Docker, ORAS, Helm, etc.)
- Built-in licensing (beta): Bind artifact (versions) to licenses for fine-grained customer access control
Getting started
Section titled “Getting started”Want a quick overview of how it works? Watch this short walkthrough:
Artifact Registry UI
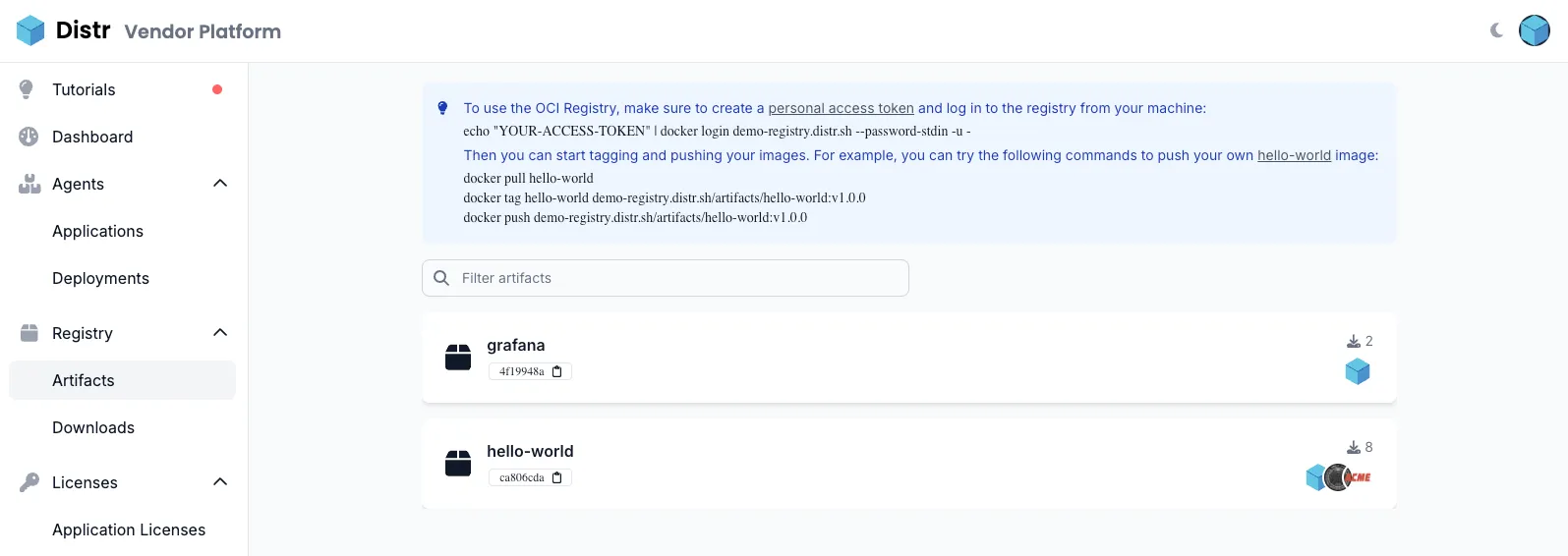
Section titled “Artifact Registry UI”Artifact List
Section titled “Artifact List”The Artifact List page lets you view all artifacts stored in your registry. It provides an overview of pull counts across all tags, along with insights into which users and customers are using each artifact.
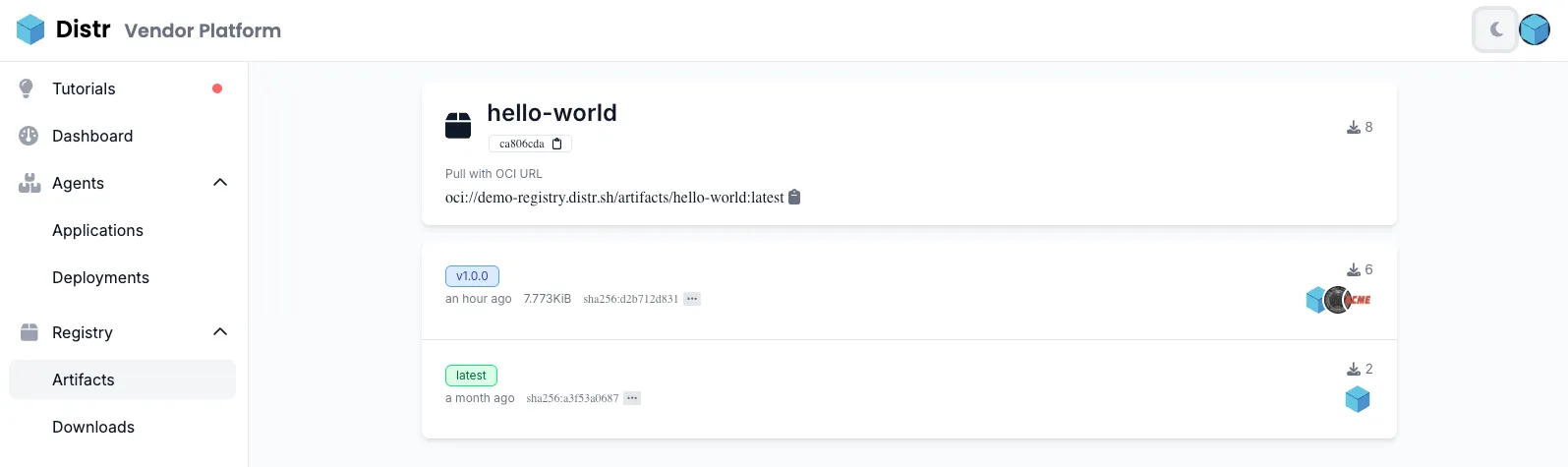
Artifact Details
Section titled “Artifact Details”The artifact details page gives you a complete view of all tags associated with a specific artifact. You can see the OCI URL, upload date, and artifact size, along with pull counts for each tag.
Artifact Downloads
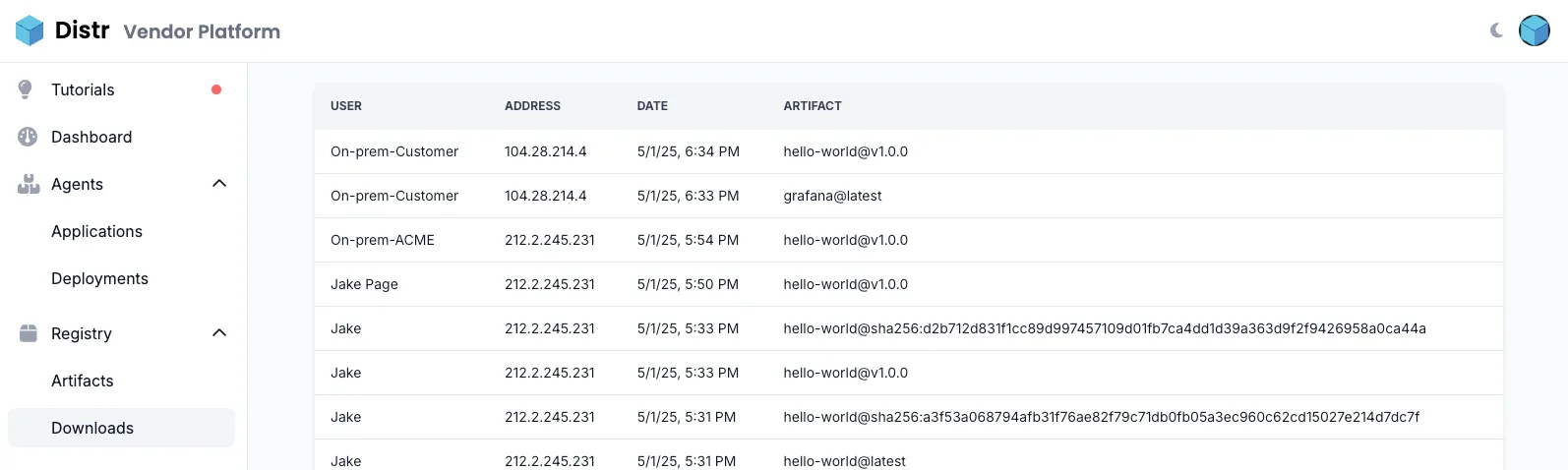
Section titled “Artifact Downloads”The Downloads section shows a chronological list of all downloaded artifacts, including which user downloaded them and from which IP address.
Global Dashboard Artifact View
Section titled “Global Dashboard Artifact View”The main Distr dashboard also provides a global view of which artifacts each end customer has consumed, including version details and a health status.
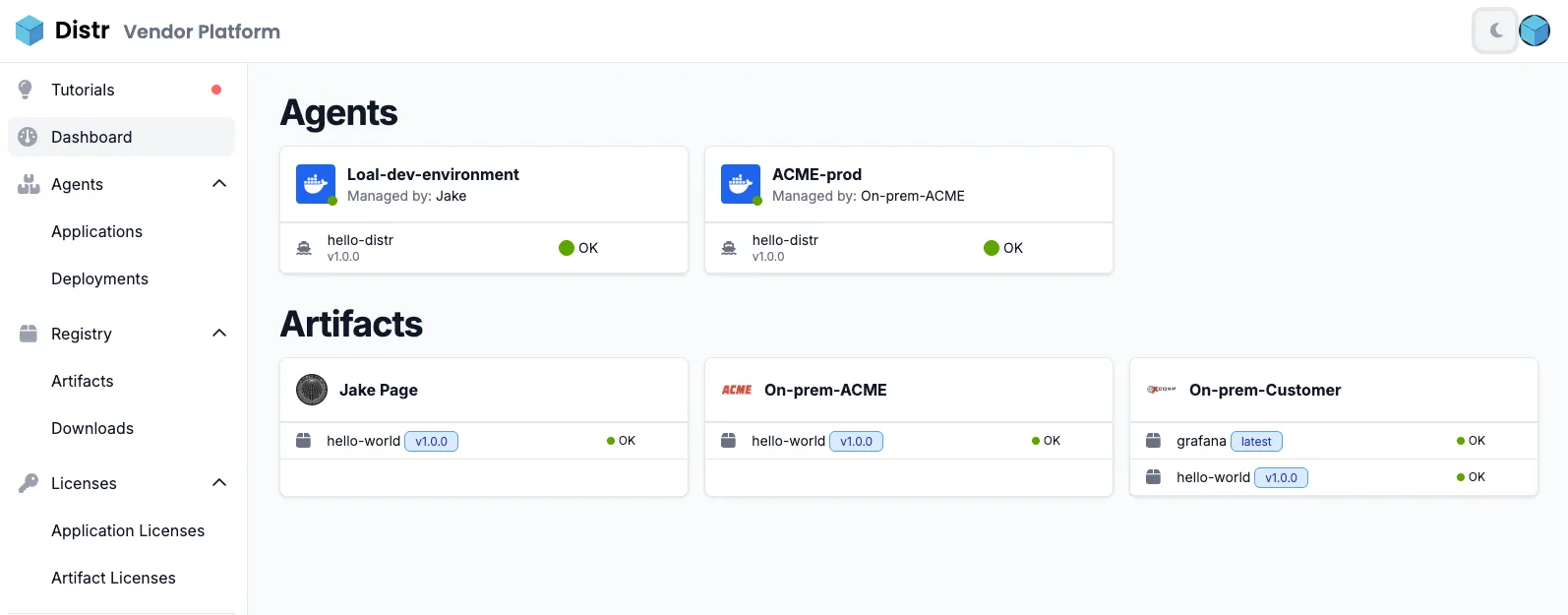
Artifact Deletion
Section titled “Artifact Deletion”The Distr registry includes sophisticated deletion logic to protect artifacts and tags that are actively referenced in licenses, ensuring customers maintain access to their licensed software.
Deleting Artifact Tags
Section titled “Deleting Artifact Tags”You can delete individual tags from an artifact through the API and UI. However, the system enforces several validation rules to prevent breaking customer access.
When Tag Deletion is Allowed
Section titled “When Tag Deletion is Allowed”Tag deletion succeeds when all of these conditions are met:
- The tag exists and is not referenced in any artifact license
- If the underlying manifest digest is referenced in licenses, other non-SHA tags must exist for that digest
Example: Tag Deletion Scenarios
Section titled “Example: Tag Deletion Scenarios”Scenario 1: Safe deletion
Artifact: myapp Tags: v1.0.0, v1.0.1, latest (all point to different digests) License: References sha256:abc123 (v1.0.0’s digest)
Action: Delete tag “v1.0.1” Result: Success - v1.0.1 is not licensed and not the last tag
Scenario 2: Blocked deletion - licensed digest
Artifact: myapp Tags: v1.0.0 (points to sha256:abc123) License: References sha256:abc123
Action: Delete tag “v1.0.0” Result: Blocked (400) - Cannot delete last non-SHA tag for licensed digest
Scenario 3: Blocked deletion - last tag
Artifact: myapp Tags: v1.0.0 (only tag remaining) No licenses
Action: Delete tag “v1.0.0” Result: Blocked (409) - At least one tag must remain
Deleting Artifacts
Section titled “Deleting Artifacts”You can delete entire artifacts from your registry, which will cascade to all associated versions, tags and historical download data.
When Artifact Deletion is Allowed
Section titled “When Artifact Deletion is Allowed”Artifacts can be deleted when they are not referenced in any active licenses.
Best Practices
Section titled “Best Practices”- Check licenses first: Before deleting artifacts or tags, verify they are not referenced in customer licenses
- Use caution with tags: Deleting tags can affect customer access if not done carefully
- Monitor usage: Review the Downloads section to understand which artifacts and versions are actively used
- Keep at least one tag: The system requires at least one non-SHA tag per artifact to maintain discoverability